Azure Digital Twins is an advanced IoT platform provided by Microsoft that enables the creation of comprehensive digital models of physical environments. These models, known as digital twins, represent real-world entities and their interrelationships, facilitating intricate simulations and real-time monitoring. By leveraging Azure Digital Twins, researchers and engineers can analyze complex systems such as smart cities, industrial facilities, and healthcare environments with unparalleled precision. The platform integrates seamlessly with other Azure services like Azure IoT Hub, Azure Machine Learning, and Azure Synapse Analytics, allowing for robust data ingestion, processing, and intelligent analytics. This interoperability ensures that digital twins can harness vast amounts of data to generate actionable insights, optimize operations, and predict potential failures before they occur. For a detailed architectural overview, refer to the Azure Digital Twins documentation.
Azure Digital Twin uses a graph-based data model to represent the relationships between objects and devices in the physical environment. This data model can be used to create sophisticated simulations and analyses of the environment, including predictions about how the environment will behave in different scenarios.
The scientific applications of Azure Digital Twins extend to various domains, including urban planning, energy management, and personalized medicine. In smart cities, digital twins can model traffic flows, energy consumption, and environmental conditions, enabling city planners to implement sustainable and efficient solutions. In industrial settings, digital twins facilitate predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity by simulating machinery behavior under different conditions. Additionally, in healthcare, digital twins can represent patient-specific models, allowing for personalized treatment plans and real-time health monitoring. The platform’s capability to visualize complex data through interactive 3D models and dashboards (see example images on the Azure Digital Twins gallery) further enhances its utility, making it an indispensable tool for scientists and engineers seeking to bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds. The integration of AI and machine learning within Azure Digital Twins also empowers users to develop sophisticated algorithms that can autonomously adapt and respond to dynamic environments, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in digital simulation and real-time decision-making.
Quick and dirty – Twin creation (testing)
Create the Digital Twins instance within an exiting resource group in Azure
Note: The --name must be globally unique across Azure.
DIGITAL_TWINS_NAME="MyDigitalTwinsInstance"
az dt create --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $DIGITAL_TWINS_NAME --location $LOCATION
Define a Digital Twins Definition Language (DTDL) Model
Create a DTDL model JSON file. For example, create a file named building.json with the following content (simple example below)
{
"@id": "dtmi:example:Building;1",
"@type": "Interface",
"displayName": "Building",
"contents": [
{
"@type": "Property",
"name": "Name",
"schema": "string"
},
{
"@type": "Property",
"name": "FloorCount",
"schema": "integer"
}
]
}Upload and Verify the DTDL Model to Azure Digital Twins
Use the Azure CLI to upload the DTDL model to your Digital Twins instance.
MODEL_ID="dtmi:example:Building;1"
az dt model create --dt-name $DIGITAL_TWINS_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --models building.json
az dt model list --dt-name $DIGITAL_TWINS_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --output jsonCreate a Digital Twin Instance and Verify its creation
Create an instance of the digital twin based on the uploaded model.
TWIN_ID="Building1"
az dt twin create --dt-name $DIGITAL_TWINS_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --twin-id $TWIN_ID --payload '{
"$metadata": {
"$model": "dtmi:example:Building;1"
},
"Name": "Headquarters",
"FloorCount": 10
}'
az dt twin show --dt-name $DIGITAL_TWINS_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --twin-id $TWIN_ID --output jsonFeatures and usage
Azure Digital Twins offers an open modeling language that enables users to create custom domain models of any connected environment using the Digital Twins Definition Language (DTDL). This modeling capability allows users to define the characteristics, properties, and relationships of real-world entities, which can be tailored to represent complex systems and environments. By providing flexibility in defining these models, Azure Digital Twins facilitates the creation of highly customized digital twins that precisely mirror the physical systems they represent.
The platform also includes a live execution environment, which brings digital twins to life by representing them in a dynamic, live graph. This environment visualizes the interconnections and interactions between various entities, allowing users to monitor and analyze real-time operations. By continuously updating the state of each entity within the digital twin, this live representation enables real-time decision-making and system optimization.
Azure Digital Twins integrates input from IoT and business systems, connecting physical assets, such as IoT devices, with business logic via services like Azure IoT Hub, Logic Apps, and REST APIs. This connectivity allows for seamless data flow between physical devices and digital models, ensuring that the digital twin remains synchronized with real-world conditions and enabling data-driven insights and automation across environments.
Azure Digital Twins can output twin change events to a variety of downstream services, including Azure Data Explorer, Azure Synapse Analytics, Event Hubs, and more. These outputs allow users to further process, analyze, and visualize the data generated by their digital twins, integrating it into larger analytics workflows, predictive modeling, or business intelligence systems, and enabling advanced insights across various sectors and industries.
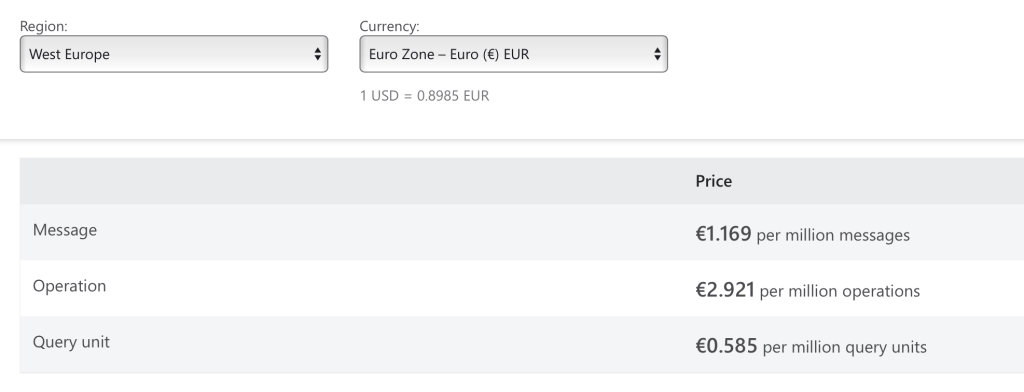
Costs
With Azure Digital Twins, there is no upfront cost or termination fee. Customers only pay for what they consume. For billing in Azure Digital Twins, there are three pricing dimensions – Operations, Messages and Query Units. The consumption of Azure Digital Twins is measured in the number of Operations, Messages and Query Units consumed. The billing is generated monthly and customers are billed on the number of Operations, Messages, and Query Units consumed during the month.
Graph-based data modelling
A graph-based data model is a way of organizing and representing data in a graphical format, using nodes and edges to represent the relationships between data points.
In a graph-based data model, the data points are represented as nodes, and the relationships between them are represented as edges. The nodes represent the individual data points, such as people, places, or things, and the edges represent the relationships between them, such as “is a parent of” or “works for.”
One of the main benefits of a graph-based data model is that it allows for complex relationships between data points to be represented in a clear and intuitive way. For example, in a social network, a graph-based data model could be used to represent the relationships between people, such as who is friends with whom, who works for whom, or who is related to whom.
In addition to representing relationships, a graph-based data model can also be used to represent the attributes of a data point, such as its name, age, or location. These attributes can be attached to the nodes in the graph, allowing for more detailed and accurate representation of the data.
Overall, a graph-based data model is a powerful tool for representing complex relationships between data points, and is widely used in fields such as data science, computer science, and artificial intelligence.
Usecases
Azure Digital Twin is a powerful tool for modeling and simulating physical environments and connected devices in the Internet of Things (IoT). It can be used in a variety of applications, including:
- Facility management: Azure Digital Twin can be used to model and simulate the behavior of a building or facility, including the relationships and interactions between different systems and devices. This can be used to optimize the performance of the facility and improve energy efficiency.
- Smart cities: Azure Digital Twin can be used to model and simulate the behavior of a city, including the relationships and interactions between different systems and devices. This can be used to optimize the performance of the city and improve the quality of life for its residents.
- Industrial IoT: Azure Digital Twin can be used to model and simulate the behavior of industrial environments and systems, including manufacturing facilities, supply chains, and transportation systems. This can be used to optimize the performance of these systems and improve efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance: Azure Digital Twin can be used to model and simulate the behavior of devices and systems over time, allowing users to predict when maintenance will be needed and plan accordingly.
- Supply chain optimization: Azure Digital Twin can be used to model and simulate the behavior of a supply chain, including the relationships and interactions between different systems and devices. This can be used to optimize the performance of the supply chain and improve efficiency.
Overall, Azure Digital Twin is a versatile tool that can be used in a variety of applications to model, simulate, and manage physical environments and connected devices in the IoT.


Leave a comment